Pimples are often a source of frustration and something curious about them is that they sometimes pop twice, but why? It’s already hard enough on us knowing that it probably might scar, but for it to pop again after the pimple has already started to heal? Essentially it boils down to the pimple or zit not fulling draining in the first pop, but there are many ways to prevent this from happening and we’ll discuss it today in this article.
First of all, zits, or pimples, are a type of acne that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. When the clogged pore becomes infected with bacteria, it can lead to inflammation, redness, and pus-filled bumps.
Understanding why zits pop twice requires an understanding of the different stages of acne development. When a zit first appears, it is in the early stages of development and is filled with pus. As the immune system works to fight off the infection, the pus-filled head of the zit may burst, releasing the pus and reducing inflammation. However, sometimes the zit may not fully drain, and a small amount of pus may remain inside. This can lead to a second pop as the immune system continues to fight off the infection.
Understanding Acne and Zits

Causes of Acne Formation
Acne is a very common skin condition that millions of people worldwide deal with everyday. There are so many factors that can cause it from excess sebum, dead skin cells, hormonal changes, and bacteria. Hormonal acne is often caused by puberty and pregnancy, but many adults experience it throughout their lives too.
The Anatomy of a Zit
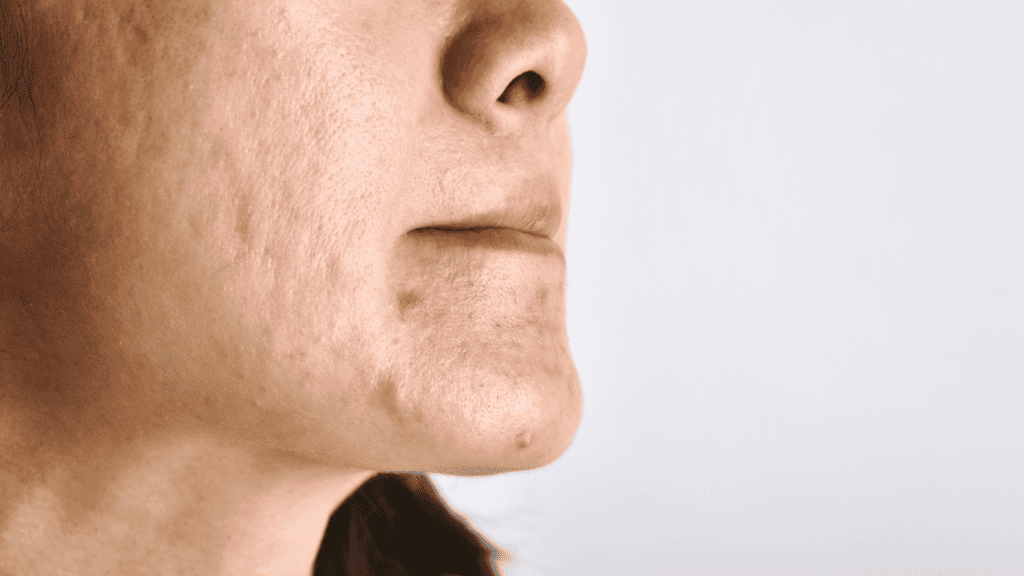
A zit, also known as a pimple, is a small inflammation on the skin that occurs when a hair follicle becomes clogged with dead skin cells, sebum, and bacteria. There are two types of pimples: comedones and pustules. Comedones are non-inflamed and can be open (blackheads) or closed (whiteheads). Pustules, on the other hand, are inflamed and contain pus.
Why Zits Pop Twice and how to Prevent it
Zits can pop twice due to the pressure applied during the first pop and if the zit was “ready” when the first pop happened. When a zit is popped, the contents are pushed out, and the skin around the area becomes inflamed. If you apply too much pressure, your skin around the pimple might be damaged and the pus that releases, could infect the area around the pimple. Also, if the pimple was popped before it was “ready” (when you can see the whitehead of a pimple), this increases the chances of pus not being fully drained as it is too deep within the skin. It is what is known as a blind pimple. If pus is not fully drained and the pimple closes, the zit will most likely pop once more.
It is important to note that popping a zit can lead to infection and scarring. Dermatologists recommend avoiding popping pimples and instead opting for treatment options such as topical or oral medications. These treatments can help reduce inflammation, kill bacteria, and prevent future breakouts.
Read More: Where does the pus go if you don’t pop it?
Proper Zit Management
Proper zit management is essential to prevent scarring and infection. There are several treatment options available, including over-the-counter products and prescription medications.
Treatment Options
Over-the-counter products containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid can be effective in treating mild to moderate acne as they work by unclogging pores and reducing inflammation.
For more severe acne, prescription medications such as antibiotics, retinoids, and birth control pills may be necessary. These medications work by reducing inflammation, killing bacteria, and regulating hormones.
Preventing Scarring and Infection
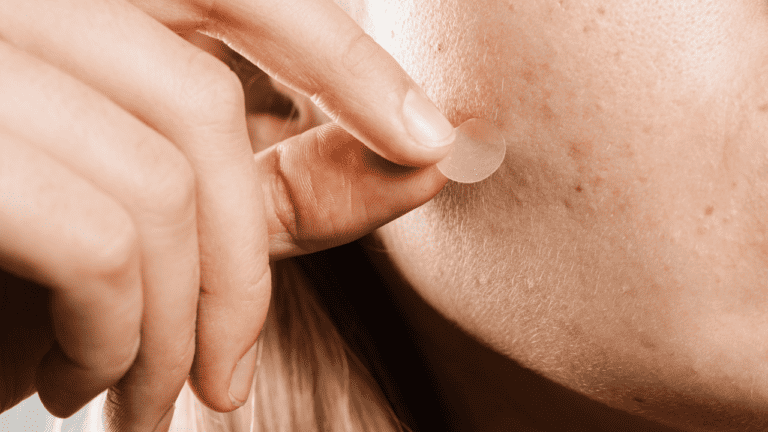
One of the most important aspects of proper zit management is preventing scarring and infection. Avoid squeezing or picking at pimples, as this can lead to scarring and spread bacteria. If a pimple must be popped, use a hydrocolloid bandage to absorb excess fluid and avoid touching it with bare hands. It is also important to sterilize any tools used to pop a pimple. This is also the case if a pimple pops by itself, just make sure to clean up the area and try to prevent the pus from touching any other areas of your face. In addition if you can use a hydrocolloid pimple patch to cover the wound, it could help speed up the healing process.
When to See a Dermatologist
If acne is severe or persistent, it may be necessary to see a dermatologist. Dermatologists can provide more aggressive treatment options such as corticosteroid injections, laser therapy, or extraction of cysts and nodules. They can also help prevent scarring and infection by providing proper treatment and advice.
In conclusion, proper zit management is essential to prevent scarring and infection. There are several treatment options available, including over-the-counter products and prescription medications. It is important to avoid squeezing or picking at pimples and to see a dermatologist if acne is severe or persistent.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes a pimple to refill after being popped?
When a pimple is popped, it creates an opening in the skin. This opening can allow bacteria and other debris to enter the pore, leading to inflammation and the formation of a new pimple. Additionally, if the pimple is not completely emptied of its contents, it can refill with fluid and become reinfected. This is why it is important to properly clean and disinfect the area after popping a pimple, to prevent further infection and inflammation.
How can you safely handle a pimple that keeps refilling with fluid?
It is important to avoid squeezing or picking at the pimple, as this can introduce more bacteria and cause further inflammation. Instead, apply a warm compress to the area to help bring the fluid to the surface. Then, use a clean, sterile needle to gently puncture the pimple and allow the fluid to drain out. Be sure to clean the area with an antiseptic solution and apply a topical antibiotic or other acne treatment to help prevent further infection.
What is the reason for a pimple to have multiple heads?
When a pimple has multiple heads, it is likely that it is a cystic acne lesion. Cystic acne occurs when the infection and inflammation occur deep within the skin, rather than just at the surface. This can cause the pimple to become larger and more inflamed, and may result in multiple heads or nodules. Cystic acne can be difficult to treat and may require medical intervention, such as prescription medications or in-office procedures.